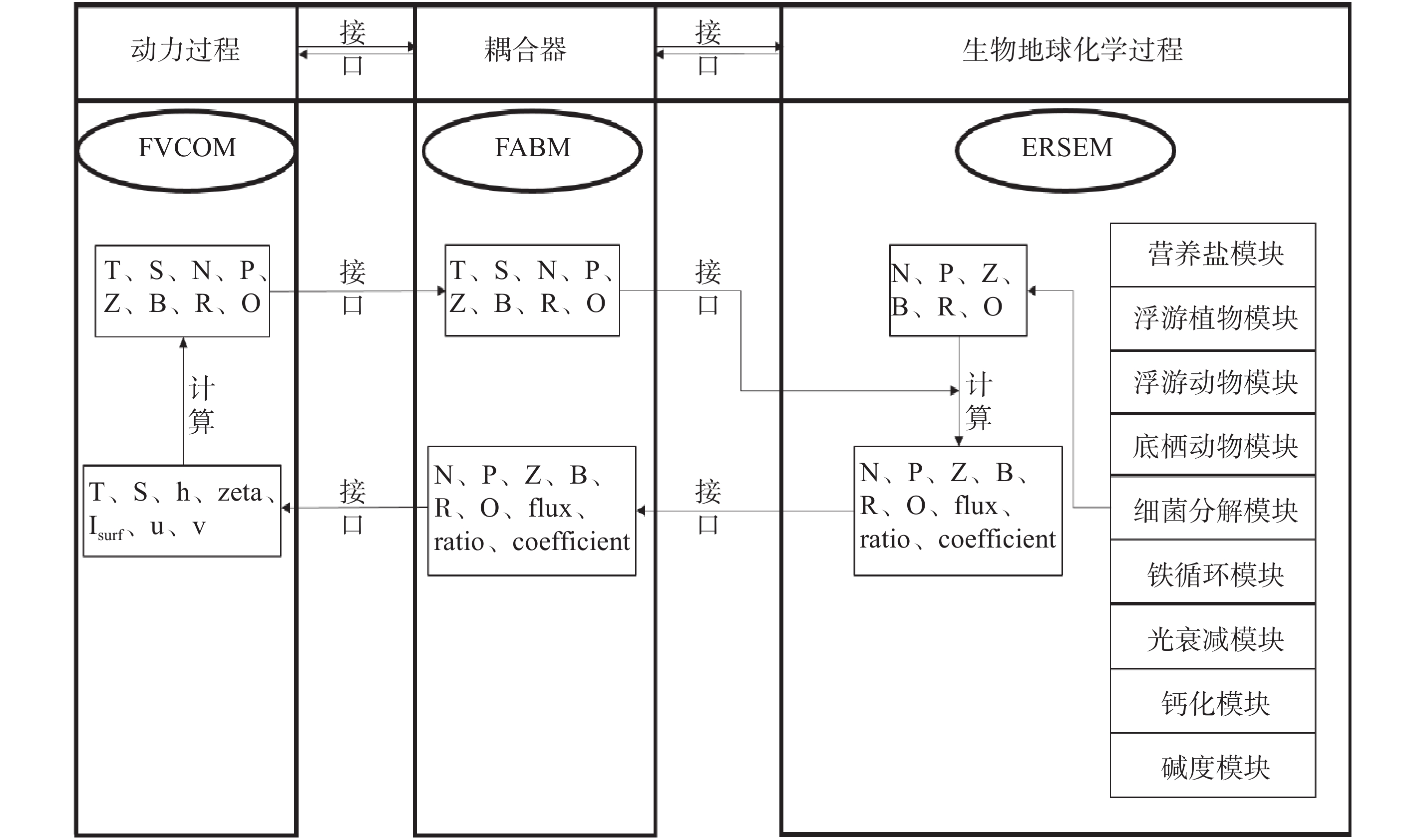
The development and application of a physical-biogeochemical coupling model based on FVCOM
-
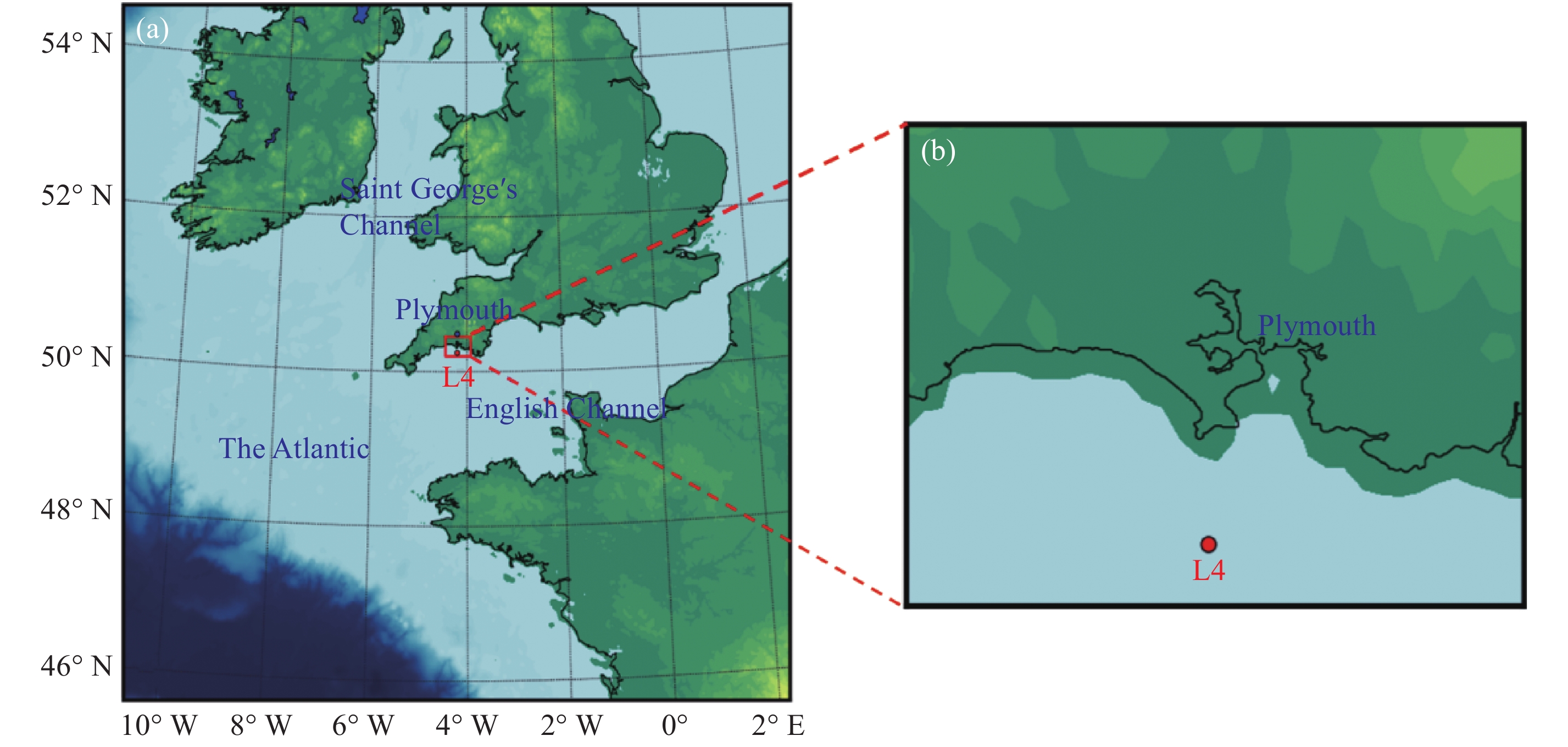
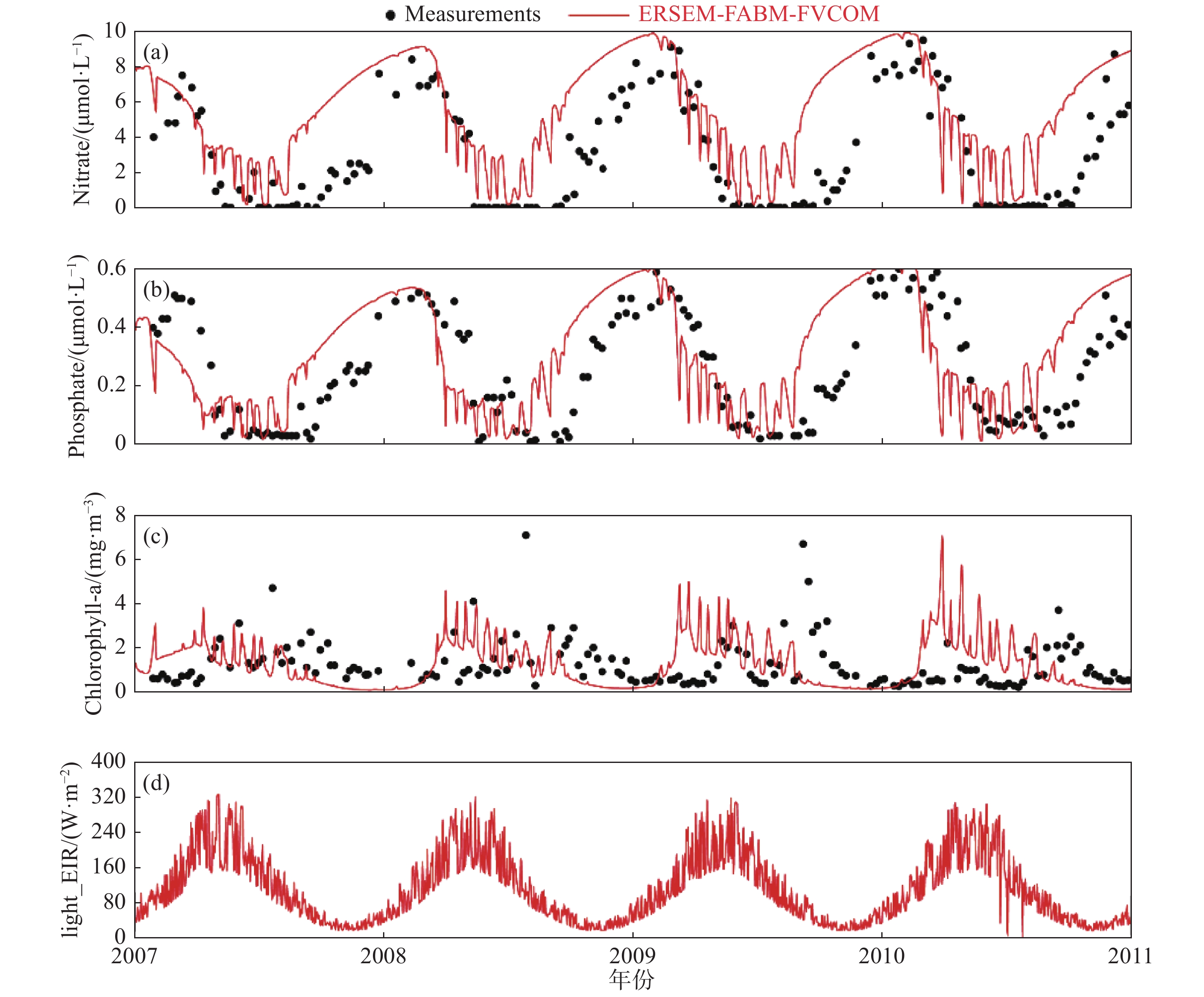
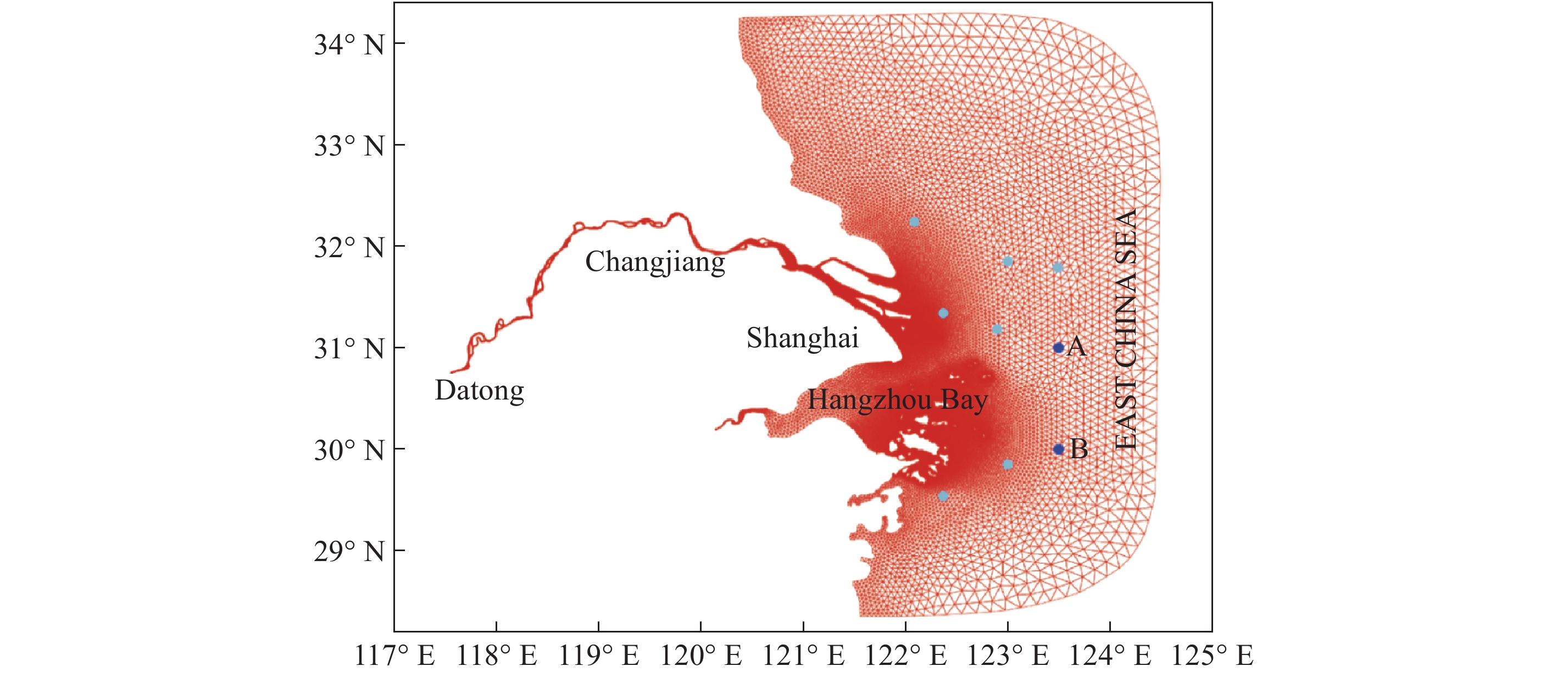
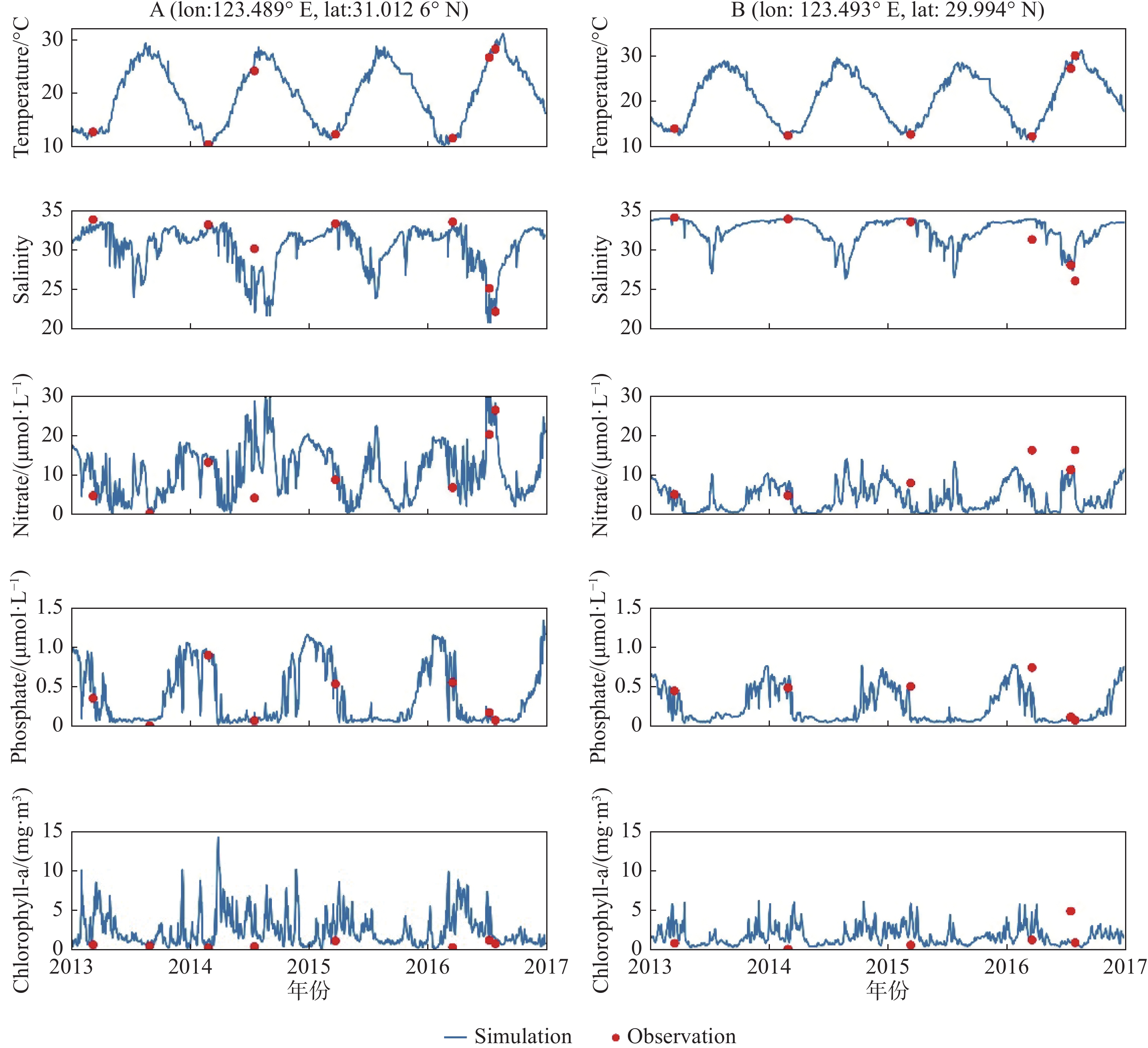
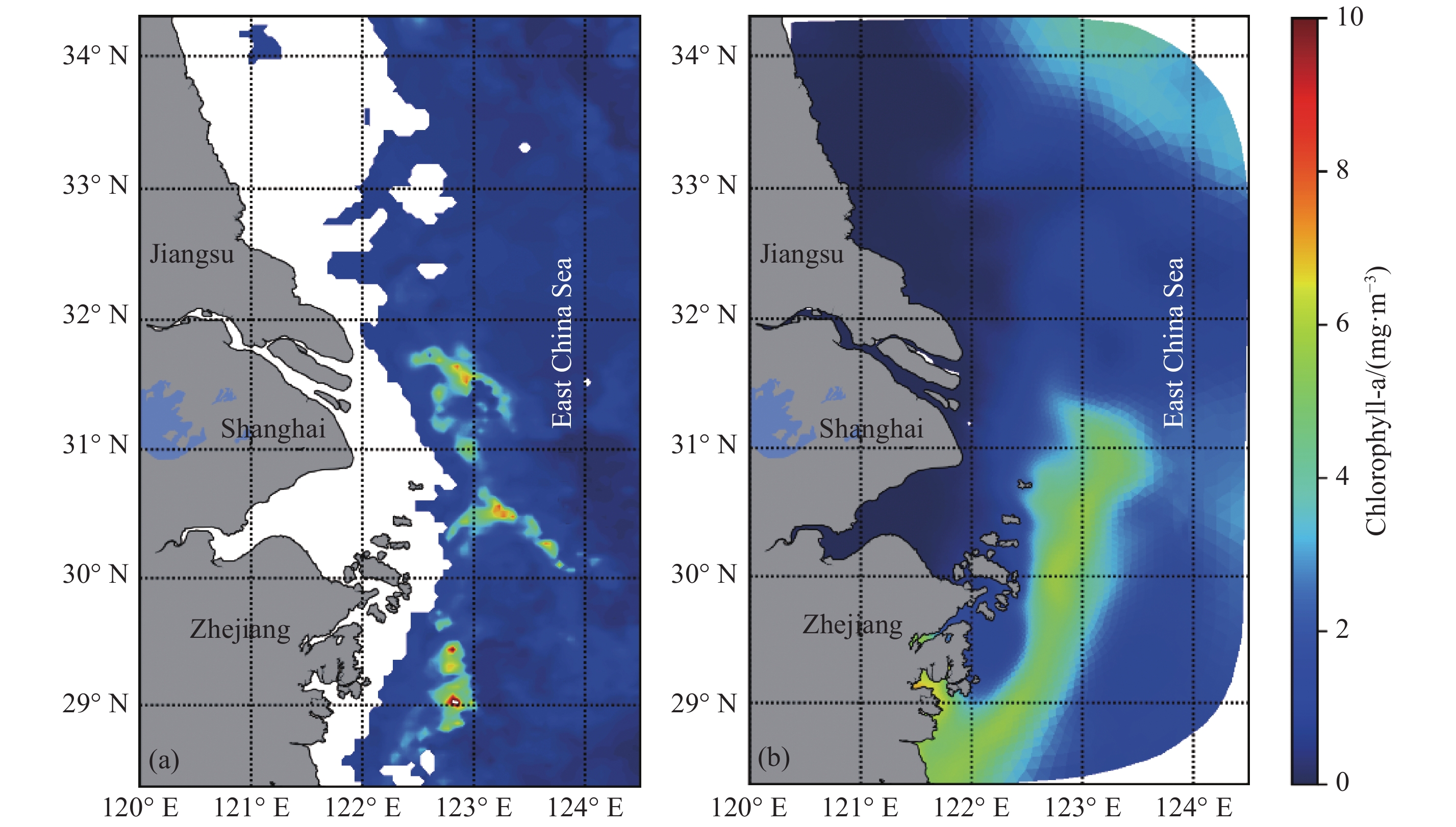
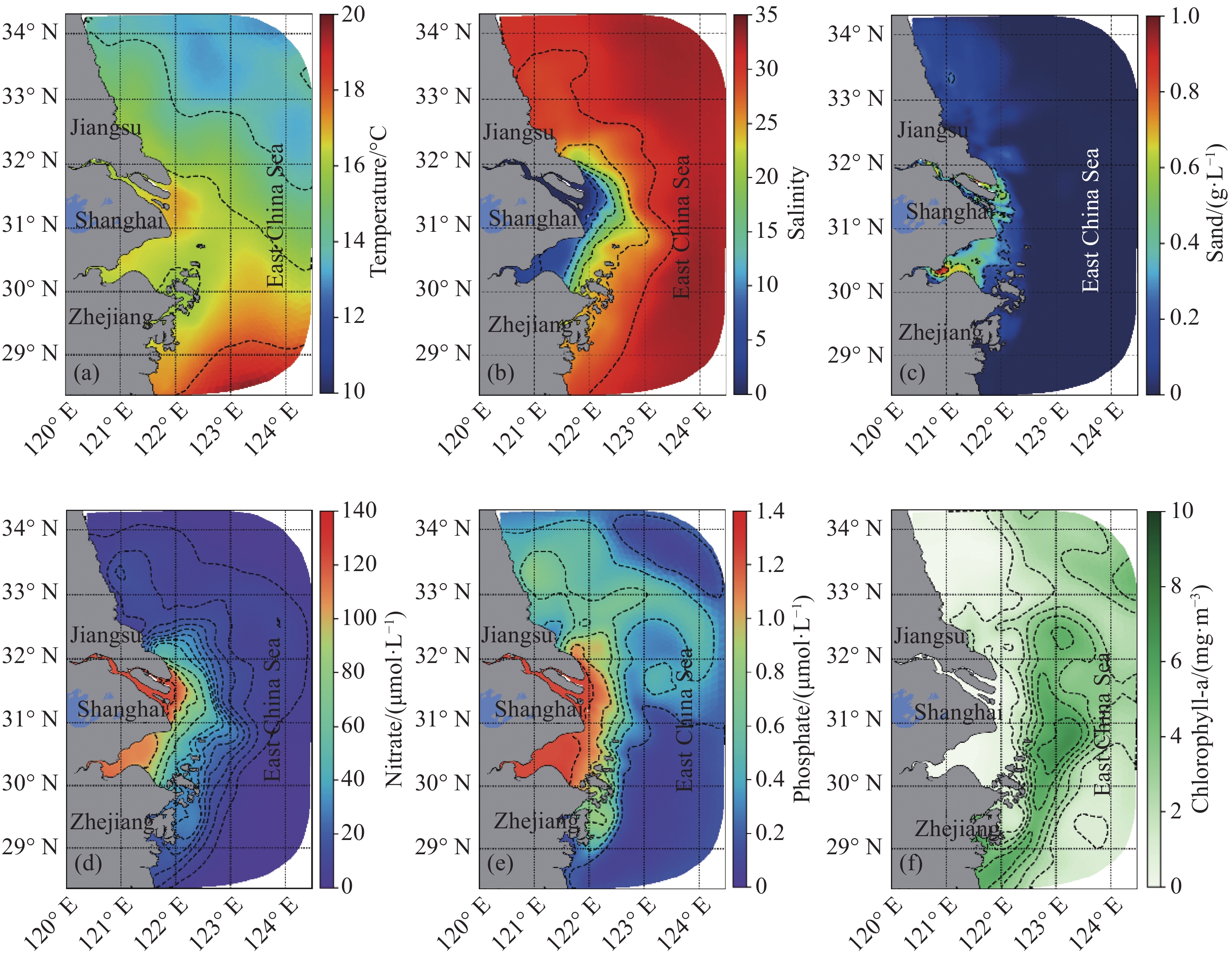
摘要: 通过使用FABM框架将水动力模型FVCOM与生态模型ERSEM进行耦合, 构建了一个新的适用于近岸复杂地形并完整描述了低营养级生态系统的物理—生物地球化学耦合模型: FVCOM-FABM-ERSEM. 基于该耦合模型分别建立了垂向一维模型和长江口三维模型. 使用欧洲L4站的多年观测资料对垂向一维模型(1DV)进行验证, 验证结果良好. 使用长江口三维模型模拟长江口及其附近海域2013—2016年的历史过程, 经与营养盐和Chl-a观测数据校验, 并利用MODIS卫星遥感的海洋表层Chl-a分布数据对春季藻类暴发的空间分布进行了验证, 证明建立的耦合模型能正确刻画长江口区域的温度、盐度、硝酸盐、磷酸盐、Chl-a等物理和生物地球化学过程. 同时, 使用模型对长江口锋面区域的特征进行了再现, 并讨论了盐度锋、泥沙锋、营养盐锋和叶绿素锋相伴产生与相互作用的关系.Abstract: By combining the hydrodynamic model FVCOM with the biological model ERSEM, based on FABM, this paper develops a new physical-biogeochemical model: FVCOM-FABM-ERSEM. The combined model is suitable for application to coastal areas and is one of the most comprehensive ecosystem models for the lower trophic levels of the marine food-web. Using the combined model, a one-dimensional vertical (1DV) model and a three-dimensional Changjiang Estuary model were established. The results of the 1DV model were consistent with observation data from the European L4 Station. This paper also simulates the physical and biogeochemical processes of Changjiang Estuary from 2013 to 2016 with the 3D Changjiang Estuary model. The distribution of temperature, salinity, nitrate, phosphate, and chlorophyll-a levels were all found to be consistent with observation data from cruises and MODIS data in the spring when algal blooms occur. The characteristics of the front dynamics of Changjiang Estuary were well represented. The relationship between salinity, turbidity, nutrients, and chlorophyll around the plume front was determined through modeling, indicating a significant co-occurrence effect along the front of physical and biological processes.
-
Key words:
- FVCOM /
- ERSEM /
- FABM /
- biogeochemical /
- coupling
-
表 1 ERSEM基本状态变量
Tab. 1 The state variables of ERSEM
浮游生态系统 底栖生态系统 P1 硅藻 R6 中型颗粒态有机质 Y2c 食碎屑动物 G4n 氮气 P2 微型浮游植物(2~20 μm) R8 大型颗粒态有机质 Y3c 滤食性动物 K5s 硅酸盐 P3 微微型浮游植物(< 2 μm) L2c* 文石 Y4c 小型底栖生物 D1m 氧层深度 P4 小型浮游植物(> 20 μm) O2o 溶解氧 H1c 好氧细菌 D2m 氧化氮层深度 Z4 中型浮游动物 O3o 溶解无机碳 H2c 厌氧细菌 D3m 难熔碳平均穿透深度 Z5 小型浮游动物 N1p 磷酸盐 Q1c 溶解有机质 D4m 难熔氮平均穿透深度 Z6 异养鞭毛虫 N3n 硝酸盐 Q6c 易分解有机质 D5m 难熔磷平均穿透深度 B1 异养细菌 N4n 铵盐 Q7c 难降解有机质 D6m 可降解碳的平均穿透深度 R1 不稳定溶解态有机质 N5s 硅酸盐 Q17c 埋藏有机质 D7m 可降解氮的平均穿透深度 R2 半不稳定有机质 N7f* 铁离子 bL2c* 文石 D8m 可降解磷的平均穿透深度 R3 半难溶有机质 bioAlk* 生物碱度 G2o 溶解氧 D9m 可降解硅的平均穿透深度 R4 小型颗粒态有机质 G3c 溶解有机碳 注: *为模型中非必须选项 -
[1] 连展, 魏泽勋, 王永刚, 等. 中国近海环流数值模拟研究综述 [J]. 海洋科学进展, 2009(2): 250-265. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.016. [2] MOLL A, RADACH G. Review of three-dimensional ecological modelling related to the North Sea shelf system [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2003, 57(2): 175-217. DOI: 10.1016/S0079-6611(03)00067-3. [3] 曲大鹏. POM海洋数值模式及对渤、黄、东海潮汐潮流模拟试验的初步分析 [D]. 山东 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2008. [4] 王彪, 朱建荣. 基于FVCOM模型的珠江河口及其邻近海域的潮汐模拟 [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012(4): 17-27. [5] LIM H, KIM C S, PARK K, et al. Down-scaled regional ocean modeling system (ROMS) for high-resolution coastal hydrodynamics in Korea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 32(9): 50-61. DOI: 10.1007/s13131-013-0352-y. [6] 储鏖. Delft3D在天文潮与风暴潮耦合数值模拟中的应用 [J]. 海洋预报, 2004(3): 29-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2004.03.005. [7] PEÑA M A, MASSON D, CALLENDAR W. Annual plankton dynamics in a coupled physical-biological model of the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2016, 146: 58-74. DOI: 10.1016/j.pocean.2016.06.002. [8] 杨金湘, 王佳. 台湾海峡冬、夏季氮通量的数值模拟研究 [J]. 海洋学报, 2018(4): 30-40. [9] LIU G, CHAI F. Seasonal and interannual variability of primary and export production in the South China Sea: A three-dimensional physical - biogeochemical model study [J]. Ices Journal of Marineence, 2009, 2(66): 420-431. [10] 郭琳. 加利福尼亚流系物理-生态过程的时空演变特征及其动力学机制研究 [D]. 山东 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015. [11] 张璇, 江毓武. 珠江口夏季底层缺氧现象的数值模拟 [J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2011(6): 1042-1046. [12] 寿玮玮. 大气沉降对渤海营养盐的贡献及生态效应 [D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018. [13] FENG T, WANG C, HOU J, et al. Effect of inter-basin water transfer on water quality in an urban lake: A combined water quality index algorithm and biophysical modelling approach [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 92: 61-71. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.044. [14] CHEN C, BEARDSLRY R C, COWLES G. An unstructured grid, Finite-Volume Community Ocean Model: FVCOM user manual[R]. SMAST/UMASSD-13-0701, 2013. [15] BUTENSCHÖN M, CLARK J. ERSEM 15.06: A generic model for marine biogeochemistry and the ecosystem dynamics of the lower trophic levels [J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2015(8): 7063-7187. [16] BRUGGEMAN J, BOLDING K. A general framework for aquatic biogeochemical models [J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2014, 61: 249-265. DOI: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.04.002. [17] 郑沛楠, 宋军, 张芳苒, 等. 常用海洋数值模式简介 [J]. 海洋预报, 2008(4): 108-120. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2008.04.016. [18] XIE Y, TILSTONE G H, WIDDICOMBE C, et al. Effect of increases in temperature and nutrients on phytoplankton community structure and photosynthesis in the western English Channel [J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2015, 519: 61-73. DOI: 10.3354/meps11101. [19] CHEN C, LIU H, BEARDSLEY R C. An unstructured grid, Finite-Volume, Three-Dimensional, Primitive Equations Ocean Model: Application to coastal ocean and estuaries [J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2003, 20(1): 159-186. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)020<0159:AUGFVT>2.0.CO;2. [20] 宋洪军, 季如宝, 王宗灵. 近海浮游植物水华动力学和生物气候学研究综述 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2011(3): 257-265. [21] CORNES R C, JONES P D. An examination of storm activity in the northeast Atlantic region over the 1851-2003 period using the EMULATE gridded MSLP data series [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(D16). DOI: 10.1029/2011JD016007. [22] FINDLAY H S, YOOL A, NODALE M, et al. Modelling of autumn plankton bloom dynamics [J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2006, 28(2): 209-220. DOI: 10.1093/plankt/fbi114. [23] EDWARDS M, RICHARDSON A J. Impact of climate change on marine pelagic phenology and trophic mismatch [J]. Nature (London), 2004, 430(7002): 881-884. DOI: 10.1038/nature02808. [24] 杜胜蓝, 黄岁樑, 臧常娟, 等. 浮游植物现存量表征指标间相关性研究Ⅰ: 叶绿素a与生物量 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2011(1): 40-44. [25] 杜胜蓝, 黄岁樑, 臧常娟, 等. 浮游植物现存量表征指标间相关性研究Ⅱ: 叶绿素a与藻密度 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2011(2): 44-49. [26] GE J, CHEN C, QI J, et al. A dike-groyne algorithm in a terrain-following coordinate ocean model (FVCOM): Development, validation and application [J]. Ocean Modelling, 2012, 47: 26-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2012.01.006. [27] 陶英佳. 长江口盐水入侵自动化预报系统的设计与检验 [D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2015. [28] LEE K, TONG L T, MILLERO F J, et al. Global relationships of total alkalinity with salinity and temperature in surface waters of the world's oceans [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(19): L19605. DOI: 10.1029/2006GL027207. [29] SOKOLETSKY L, YANG X, SHEN F. MODIS-based retrieval of suspended sediment concentration and diffuse attenuation coefficient in Chinese estuarine and coastal waters [C]// Ocean Remote Sensing & Monitoring from Space. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2014. [30] LAMQUIN N, MAZERAN C, DOXARAN D, et al. Assessment of GOCI radiometric products using MERIS, MODIS and field measurements [J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2012, 47(3): 287-311. DOI: 10.1007/s12601-012-0029-z. [31] XING X, ZHAO D, LIU Y, et al. An overview of remote sensing of chlorophyll fluorescence [J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2007, 42(1): 49-59. DOI: 10.1007/BF03020910. [32] WANG K S, CHENG H, DONG L X. A hydrographic comparison of the two sides of the Changjiang plume front [C]// Proceedings of International Symposium on Biochemical Study of the Changjiang Estuary and its Adjacent Coastal Waters of the East China Sea. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990:62-75. [33] 胡方西, 胡辉, 谷国传. 长江口锋面研究 [M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 2002. [34] 闫庆. 长江口外锋区浮游植物生物量及其影响因子的观测与数值模拟 [D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016. [35] TIAN R C, HU F X, MARTIN J M. Summer nutrient fronts in the Changjiang (Yantze River) estuary [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1993, 37(1): 27-41. DOI: 10.1006/ecss.1993.1039. [36] 沈志良. 长江口海区理化环境对初级生产力的影响 [J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1993(1): 47-51. [37] 周淑青, 沈志良, 李峥, 等. 长江口最大浑浊带及邻近水域营养盐的分布特征 [J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(6): 34-42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.06.008. [38] 杨波. 三峡工程对长江口羽状锋区生物地球化学特征的影响 [D]. 山东 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2012. [39] 张传松. 长江口及邻近海域赤潮生消过程特征及其营养盐效应分析 [D]. 山东 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008. -





 下载:
下载: